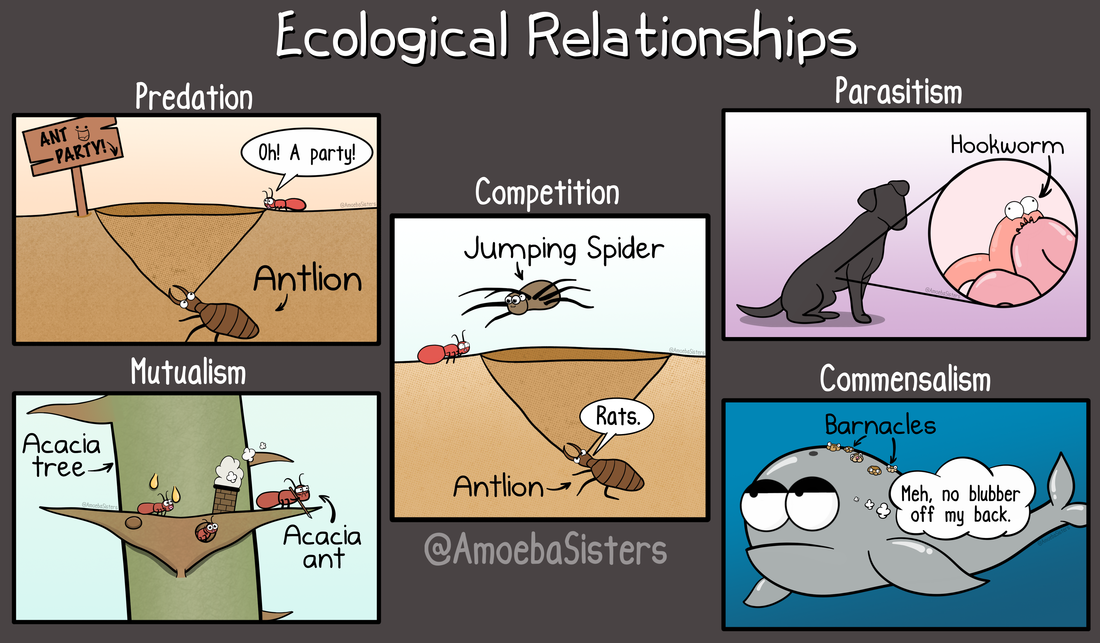
Commensalism Ecological Relationships
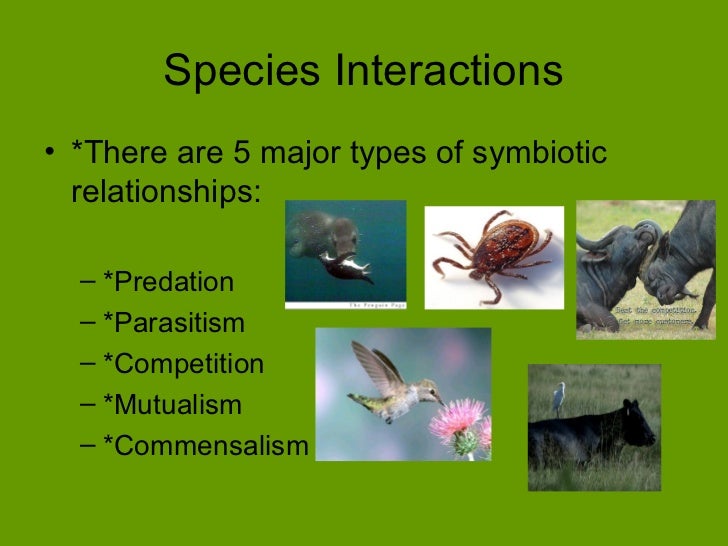
Intraspecies competition organisms competing can be from within same species for example two male fighting of elk for a female mate.

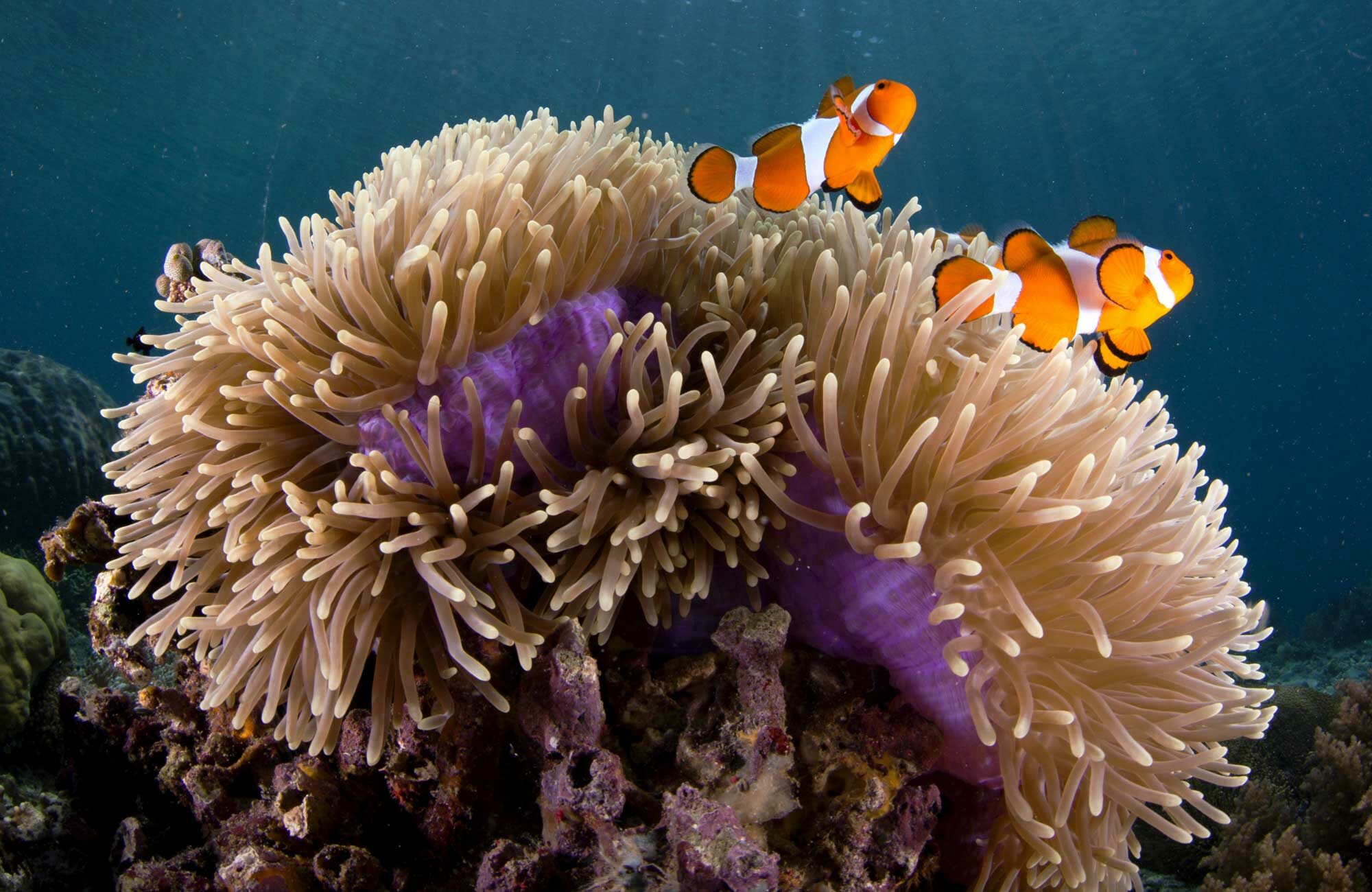
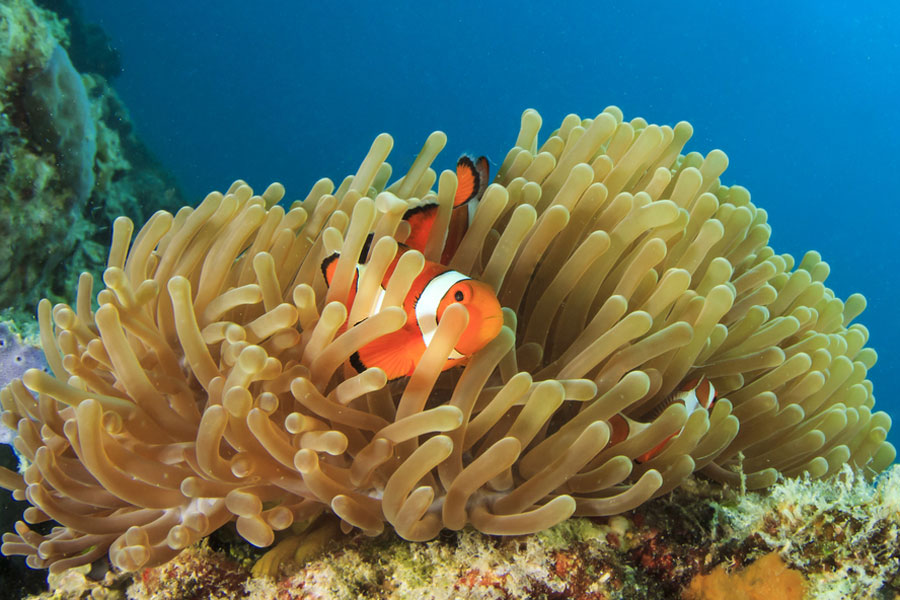
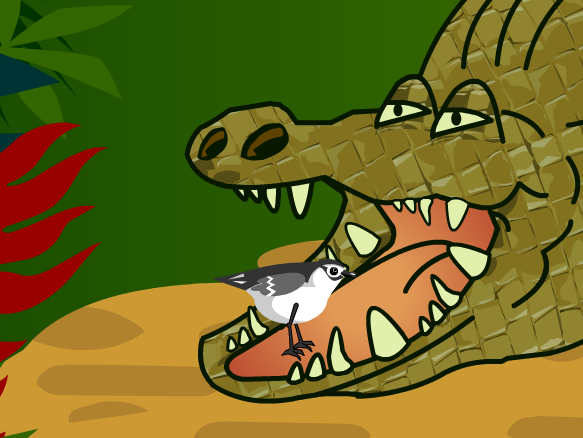
Commensalism ecological relationships. Commensalism pilot fish naucrates ductor swimming alongside a whitetip shark carcharhinus longimanus. The competition as relationship in the ecosystem the competition is when organisms compete for same resources. Commensalism is an association between two different species where one species enjoys a benefit and the other is not significantly affected.
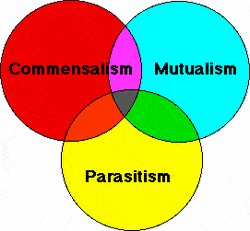
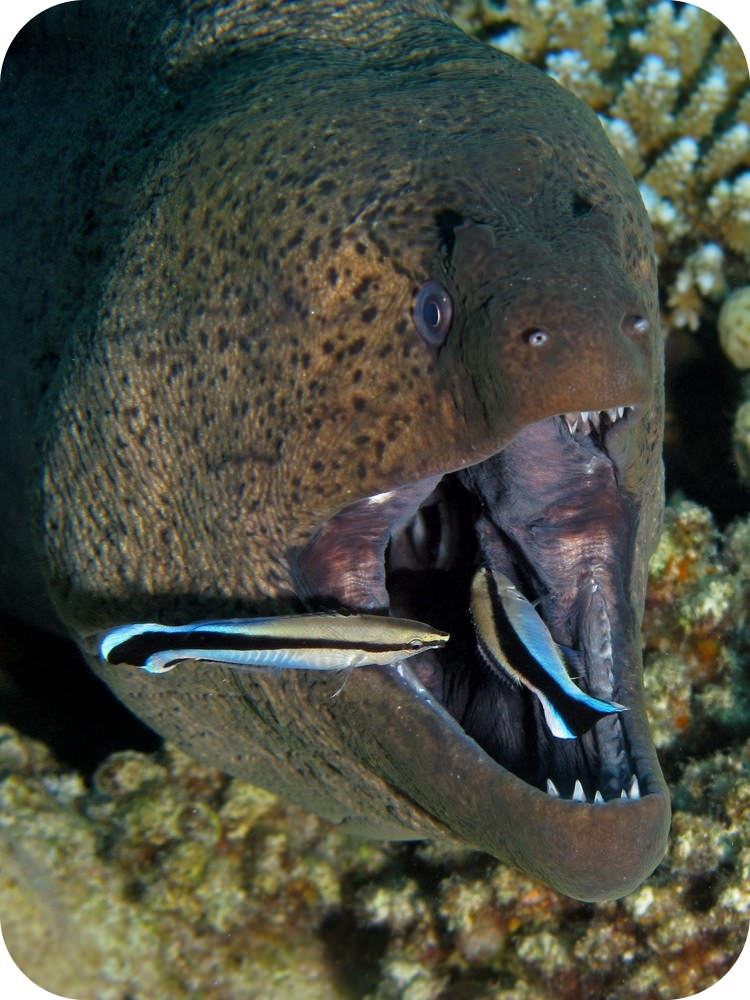
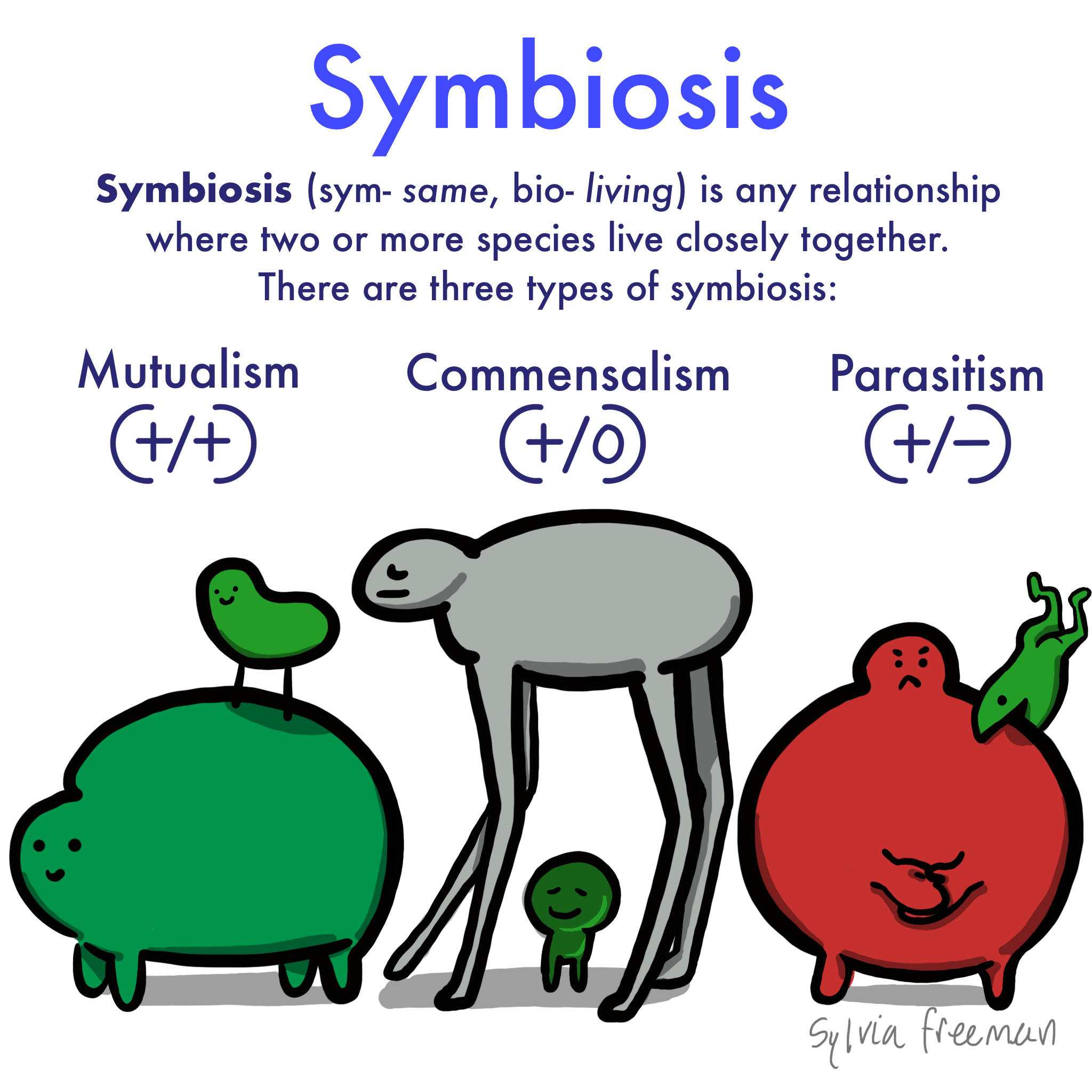
Mutualism and parasitism are more common than commensalism. Build background about national geographic crittercam. Commensalism is a long term biological interaction symbiosis in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed.
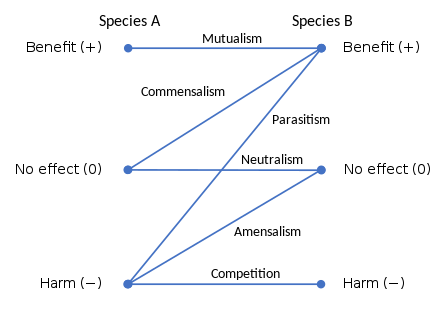
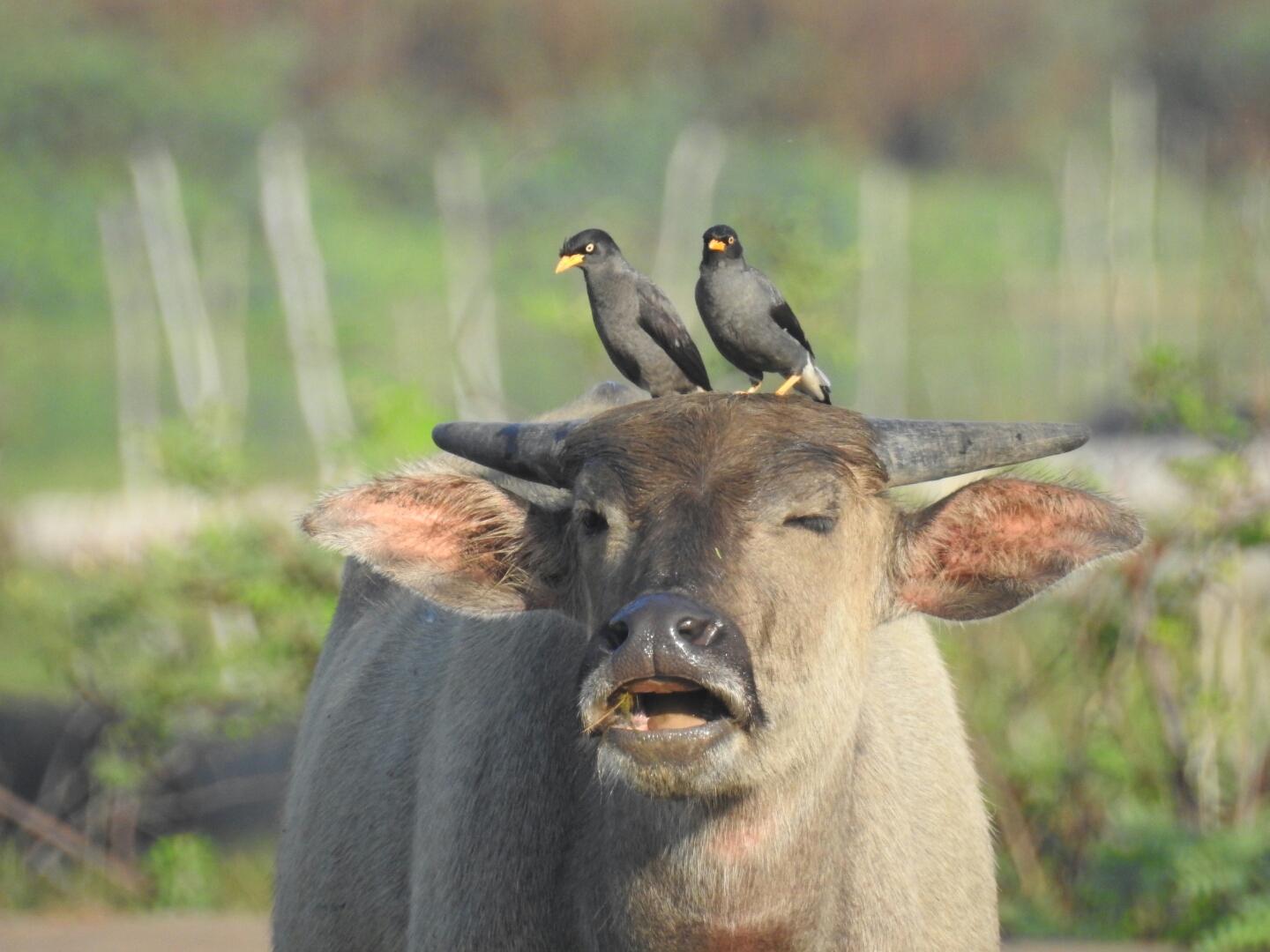
For instance egrets trail cattle to capture airborne insects that are stirred up by foraging livestock. This is in contrast with mutualism in which both organisms benefit from each other amensalism where one is harmed while the other is unaffected and parasitism where one benefits while the other is harmed. Mutualism a symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit.
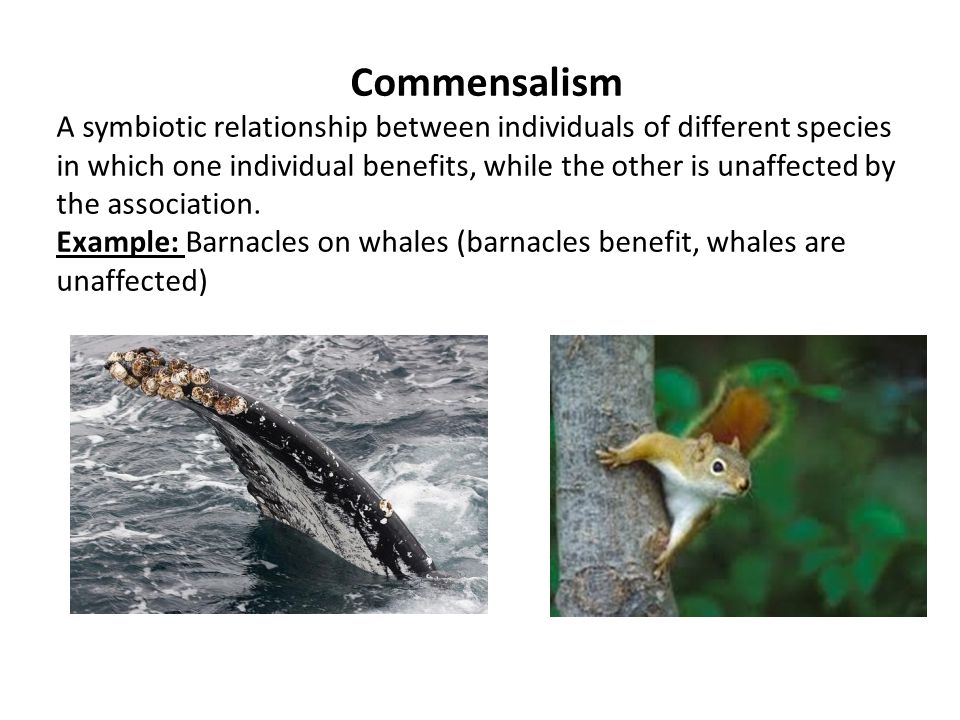
Parasitism a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and one is harmed. A commensal species benefits from another species by obtaining locomotion shelter food or support from the host species which for the most part neither benefits nor is harmed. Commensalism in biology a relationship between individuals of two species in which one species obtains food or other benefits from the other without either harming or benefiting the latter.
Symbiosis is broken down into mutualism commensalism and parasitism based on how two species interact in their ecosystem. Commensalism is a type of relationship between two living organisms in which one organism benefits from the other without harming it. This is a negative relationship because both organisms are harming each other campbell.
Commensalism in ecology is a class of relationships between two organisms where one organism benefits from the other without affecting it. In biology a symbiotic relationship is defined as a close relationship between two distinct species that persists long term. Commensalism a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and one does not benefit but is unharmed.
Mutualism is where both organisms benefit commensalism is where one benefits but the other organism isnt harmed and lastly parasitism is where one organism benefits and the other is harmed.































/commensalism-definition-and-examples-4114713-v2-706cadecce404b008d6620bb061841cc.png)











/clownfish_sea_anemone-581b994d3df78cc2e879cc71.jpg)













:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lemon_shark_remora-5a90960bff1b780037bb3d86.jpg)


































_1580989500650_1582535473834.jpg)


